Human ingenuity and creativity are the primary resources that drive the creative economy and transformative change process. - Creative Economy Report 2013
The Creative Manufacturing Program offers two distinct pathways.
Product & Furniture Design
This pathway develops a well-rounded & skilled designer who is ideally suited to design products and furniture using traditional and emerging technologies in the micro and small-scale sectors for contemporary markets.
Textile & Apparel Design
This pathway develops a creative and skilled Textile & Apparel designer who can work in the rich Indian Textile & Fashion industry to create apparel and home linen for new markets worldwide.
About the Program
The Creative Manufacturing Program aims to train young professionals to work with the traditional crafts, manufacturing, and textile industries to transform them into successful business enterprises. The program teaches a comprehensive method that combines design, business acumen and an understanding of the market to improve the design & production of creative goods.
The core content of the course focuses on:
- The ability to design to fulfil customer aspirations and industry needs & create sustainable profitability.
- A keen hands-on understanding of the material, manufacturing process and business
- Sustainable practices that are economic, environmental, social, and cultural.
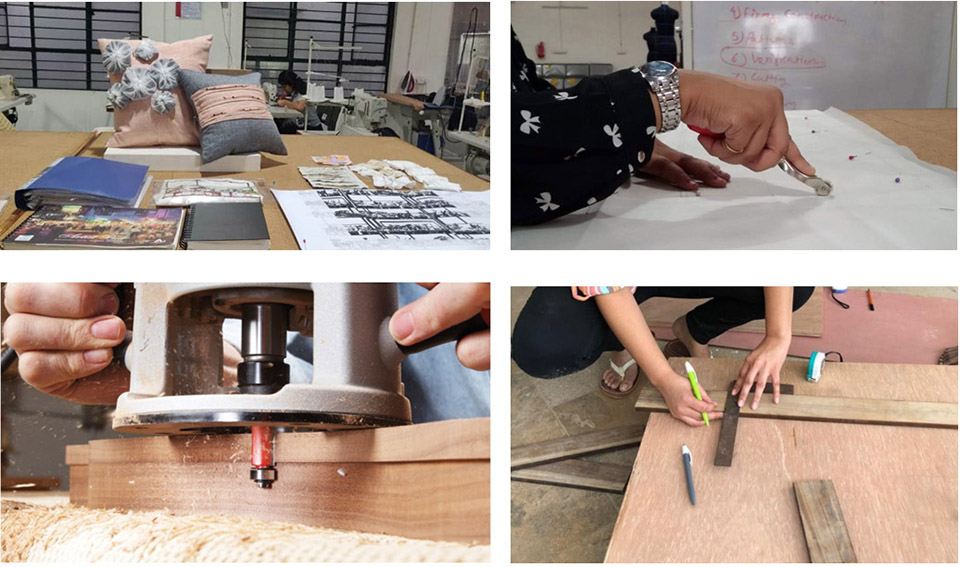
Hands-on learning
Vision
With over $500 billion in annual revenue today, the creative manufacturing and handmade (CMH) sector is projected to grow by 20% annually, reaching $1 trillion by 2024, creating a huge opportunity. India’s creative manufacturing industry has a 5000-year artisanal legacy and about 60 million workers. This growing industry needs designers who can marry business, productivity, technology, and design to create products for contemporary needs.
This program aims to train practitioners who can design for Indian and international markets for craft-based creative goods. You will learn to work hands-on in design, use of materials, production practices, business and entrepreneurship to become work-ready design practitioners. You learn to employ state-of-the-art processes, including using digital technology to impact millions of Indians and effectively transform India’s global market share in creative manufacturing.
Sector
- Furniture & Fitting Skills
- Apparel Made-Ups & Home Furnishing
- Handicrafts and Carpet
The three years of this course align with levels 4, 5, 6, and 7 of the NSQF guidelines and create skilled practitioners for the above sectors.
NSQF, or National Skills Qualifications Framework, is a nationally integrated and competency-based education framework that allows individuals to achieve their desired competence level. In NSQF, qualifications are organized according to the levels based on skills, knowledge, and aptitude.
Key Elements Of National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF):
- Skill proficiency promotion to create individuals with international equivalency
- Multiple entries and exit provisions for students
- Opportunities to help students become lifelong learners
- Preparedness for the industry standard with the development of skills
- A transparent mechanism for the growth of students

Product prototyping and documentation of work
Course Structure
The core principles that govern the design of the unit are as follows:
- Mastery Learning with Guided Practice breaks down competences or skills into subskills, methods and techniques. Through targets taught through modelling and direct instruction followed by guided and independent practice, mastery of core competences and skills are achieved.
- Work Related Learning is the co-design of opportunities/projects by industry based professionals or employers or other stakeholders on the one hand and faculty on the other. Guided and facilitated by mentors this space allows for future employers to participate in the learner’s journey.
- Industry Linkages includes both exposure, orientation and direct interactive learning in real time contexts. This is towards specific jobs and roles, as well as work experience within each course’s respective industrial sector. Linkages between academic institutions and creative industries is inclusive of both economic and social benefits of innovation.
- Fab. Ateliers builds on the values of thinking, modelling and making to challenging design contexts drawn from indigenous knowledge and / or tools from digital technology.
- Public Labs are open spaces that foster DIY thinking along with citizen science and other initiatives to build a culture of learning that is self-initiated, independent and collaborative . Public Labs are open to all learners for purposes of self-study, learning, archiving and developing personal interests in technologies
- Bootcamps foster accelerated learning of concepts, skills and technologies that are directly linked to either employable, entrepreneurial or livelihood based skills. Working through immersion, with a focus on hands-on problem solving and peer learning rather than instruction.
- Hackathons can range from competitions or events over days to half-day jams or a one day hack-fest. This format encourages brainstorming, pitching of concepts, working in teams and also planning projects as well as development of prototypes
Pathways
Creative Manufacturing offers a choice of two pathways and students can choose any one pathway to pursue:
People
Enquiries

FAQs
Creative Manufacturing is a subset of the larger creative industry, one of the fastest growing sectors globally. Creative Manufacturing is where the manufactured goods carry the mark of its maker as creative interventions. All the handicraft and textile traditions of the country fall into the Creative Manufacturing sector. The course at Srishti is offered through two pathways- ‘Product & Furniture Design’ and ‘Textile & Apparel Design’.
Around 400 years ago, India used to be the largest supplier of goods in the global market and its combined trade was more than all of Europe combined. Other than spices, almost everything that was exported out of India was from what we now call the creative manufacturing industry. Globally the demand for the hand-made and the natural is growing, but the supply is sketchy, the designs are weak and of poor quality. The growing market awaits good design, on-time delivery and high quality and therein lies the opportunity. The next generation shopper is looking to consume products that are more sustainable, less capital intensive and more socially equitable.
Creative Manufacturing goods reflect the skill of the producer and not just of the machines that are employed to produce them. The products have added value of the hand made and no two products are identical. Many of the products are also cultural in nature. Creative Manufacturing is considered more sustainable because it uses less energy, is less capital intensive, is more socially equitable (it puts more money in the hands of skilled producers), has a smaller environmental footprint because it largely uses local and natural and renewable materials.
If you like to build things that are beautiful as well as functional and take pleasure in realizing your ideas physically, this is an area you should consider. If you are independent-minded, have the ambition and drive to run your own business in the Creative Manufacturing sector that marries the creative impulse with good business, then this course will prepare you for it. You need to be curious about how things work and how they are made. This course is also very useful to applicants coming from second and third generation entrepreneurial families already in the business and who want to continue in and expand their parent’s trade.
Please download the prospectus on the course page to know about the learning units that will be taught in this course.
The ‘Products and Accessories’ pathway deals largely with products made of hard materials like metal, wood, ceramic - the focus is on hard materials. The ‘Textiles, Accessories and Made-ups’ pathway on the other hand, works largely with fibre, yarn and fabric or the soft materials. Although the focus of the two pathways are on hard and soft materials respectively, both pathways will allow students to combine materials for a specific aim.
Both these pathways require specialized training and competence building and therefore these are offered as two separate areas of learning. From the first year itself, you are required to choose your area of interest in either one of these two pathways. While there are some learning units that are common to both the pathways, you are not encouraged to change your pathway once chosen. All learning units for each of the pathways are defined and mandated.
The basics of entrepreneurship are equally important whether you are an owner, founder, manager or a designer. Entrepreneurship is a stance that is useful regardless of what you do.
Companies also value ‘intrapreneurship’ which is a relatively recent concept where an employee behaves like an owner and takes empowered decisions.
In order to be effective, a designer has to know how best to have his/her ideas produced. Understanding production is the key to making quality products on time.
‘Lean Production’ was pioneered by the Toyota Motor Company and is the most advanced method of production that optimizes the use of resources with minimum waste of material and effort. Lean methods have now moved into all forms of work including design, software, people management etc. Lean production works bottom up from workers to top management and everybody participates.
No. While the emphasis is on products, you can also learn to design and make other artefacts like toys, educational aids, décor products and even larger pieces like furniture. The pathway covers a range of materials and works with combining these.
The course will allow you to work in the industry, in several roles. Here are a few examples but they are in no way an exhaustive list as the course is designed to nurture innovation, allowing for a unique combination of skills to create new roles.
Both the pathways will prepare you to become a Design Technician, Floor Supervisor, Design Assistant to Merchandiser, Assistant Designer, Production Supervisor, Start-up Entrepreneur, Designer, Production Coordinator/Manager in the respective sectors.
If you are in a family run-business, then this course equips you to run it one day. You can also set up your own independent business.
This course will also open avenues for higher education in art, technology and design.
Please visit the two pathway webpages (‘Product & Furniture Design’ and ‘Textile & Apparel Design’) to learn more about the different employment opportunities after each year.